A letter to my Patients
Over the last few years, a new type of medication has been used to improve upon the treatment of Diabetes. Through the investigation of normally produced molecules in the healthy person, research has determined that many interactions in the body are regulated and controlled by chemicals called Peptides. In the case of glucose metabolism (which is the problem in diabetics), two peptides have been studied and used to control blood glucose, Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy and others) and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Both Semaglutide and Tirzepatide work by stimulating the Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1). Tirzepatide also includes a Glucose-dependent Insulinoptropic Polypeptide (GIP). We will discuss this in some detail later.
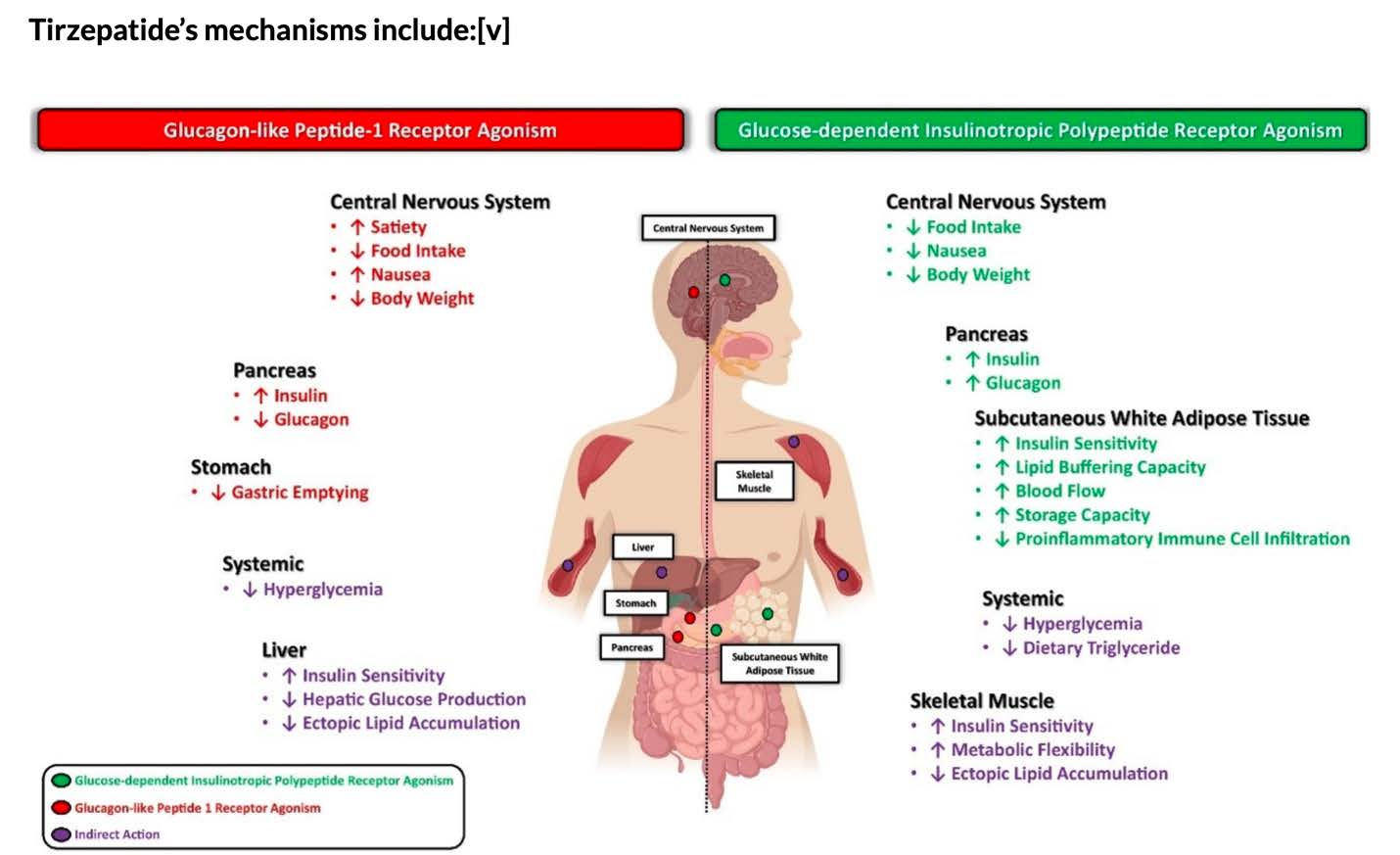
The way these peptides help control diabetes is complicated but one benefit is that they are very effective in helping patients lose weight through several mechanisms. Since obesity is one of the major causes of health issues, these medications have become a mainstay in medically supervised weight loss. These peptides work on the brain by making patients feel less hungry which helps to decrease caloric intake. GLP-1’s decrease the emptying of the stomach so you feel more full. It also works in the body to decrease serum glucose (increases insulin release and increases the body’s insulin sensitivity) and helps the liver metabolize glucose and lipids better. GIP works on the body’s fat and muscles to metabolize sugars and fats better, adding to the benefits of GLP-1. GIP also helps decrease the most common side effect of GLP-1 which is nausea. See the below diagram. Semaglutide effects the left side only.
Both of these medications can only be injected under the skin, similar to insulin. They are both weekly injections that Dr. Hause and his staff can eventually teach you how to do after a month or two of treatment. Because the response to these medications varies, patients are started on a low dose which is then titrated/adjusted to get the optimum result with the fewest side effects. GLP-1 and GIP medications are serious modulators of metabolism and must be treated with respect.
Weight loss protocols are designed for patients with Body Mass Index (BMI) over 25 who want to lose as much as 20 percent of their body weight over a period of months. Rule of thumb for healthy weight loss is approximately 10 pounds per month. These protocols require you to maintain a healthy lifestyle of activity and balanced low fat, high protein diet. Because the effect of the medication is to delay stomach emptying and modify digestion, you must be committed to maintaining hydration (drink at least 32 ounces of water per day) and eat a generous amount of dietary fiber (fruits and vegetables or dietary fiber supplements) to prevent sometimes serious constipation.
Also, because they decrease stomach emptying, they can alter the absorption of other oral medications. It is advised for women relying on oral contraceptives to use alternative methods while they are on the medication as their oral contraceptives may be less effective. Patients requiring elective surgery should stop injections 3 weeks prior to their planned surgery.
Prior to beginning injections Dr. Hause will require you get preliminary blood tests including a CBC, Complete Metabolic Panel, and Hgb A1c that is an additional cost to the patient (or you can obtain it from your primary care physician if covered by insurance). This may need to be repeated later in the treatment course. Because these medications alter glucose metabolism and may cause more serious complications in Diabetic patients, our clinic will not treat Diabetic Patients. For those with Diabetes, it is far safer to have these medications monitored by your primary care physician if it is appropriate to add this protocol to your treatment.
Absolute Contraindications (cannot be prescribed) for GLP-1 and GIP:
Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC), Patients with Family History of MTC, and Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome type 2: In some animal studies, there is evidence that GLP-1 stimulates MTC. Because of these findings, the use of GLP-1 is contraindicated for patients at risk of MTC or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome type 2 (MEN2).
Pregnancy and Breast Feeding: GLP-1 and GIP have not been studied in Pregnant women or those breastfeeding. Therefore pregnancy and breastfeeding are contraindications to these medications. By agreeing to undergo these protocols you are certifying you are not pregnant and are taking contraceptive precautions. Patients planning on becoming pregnant must be off of these medications for 3 months before becoming pregnant.
GLP-1 and GIP have not been studied in children so patients under the age of 18 will not be candidates for these protocols.
Possible Risks and Side Effects:
- The local injection site can have bruising, bleeding, and local redness. Rarely there can be skin infections.
- Gastrointestinal Upset: Because of the effect on stomach emptying and the slowing of digestion, the most common side effects of treatment are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, indigestion, belching, feeling bloated, and abdominal discomfort. This can occur in as much as 18% of patients. Slow titration/adjustment of dosing may help these symptoms but in some patients, this may make taking the medication unworkable. It is critical to maintain good hydration and the consumption of fiber to prevent constipation. In rare cases, the patient can experience the severe complication of ileus (blockage of the intestines) requiring hospitalization and even surgery. If you experience persistent, unrelieved constipation, abdominal bloating, cramping, the inability to pass gas, and vomiting you should seek immediate medical attention.
- Fatigue, Dizziness, and Headache: Some patients experience fatigue, dizziness, and headache, which may be a result of low blood sugar.
- Low Blood Sugar: There is an increased risk of Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, rapid heartbeat, mood changes, irritability, weakness, shakiness, slurred speech, confusion, and profound hunger. Treatment requires the patient to consume simple sugars such as candy, sugar soda, or orange juice. In severe cases, emergency hospitalization is warranted.
- Allergic Reaction or Hypersensitivity: Although rare, allergic reactions or serious hypersensitivity may occur. Signs may include hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Immediate treatment may be necessary should this occur.
- Runny Nose and Sore Throat: A common complaint is a runny nose and sore throat.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the Pancreas (Pancreatitis) rarely occurs and can be very serious. Symptoms would include persistent severe abdominal pain in your stomach with or without vomiting.
- Gallbladder Inflammation or Gallstones: Because of dehydration and the slowing down of digestion, gallstone disease can be exacerbated. If you have persistent upper abdomen pain in the right side especially after eating, seek medical attention.
- Changes in Vision: Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy may experience temporary visual changes from the reduction of blood glucose. Please report any changes to your physician.
- Dehydration and Kidney Damage: There is a potential risk of severe dehydration and acute kidney injury and renal impairment. It is important to stay well hydrated if injecting GLP-1 and GIP.
